摘要
JDK:1.8.0_202
SpringBoot Version:2.3.2.RELEASE
示例代码:configure-demo (opens new window)
# 一:前言
Spring Boot获取文件总的来说有三种方式,分别是 @Value 注解,@ConfigurationProperties 注解和 Environment 接口。这三种注解可以配合着 @PropertySource 来使用,@PropertySource主要是用来指定具体的配置文件
# 二:@PropertySource解析
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
/**
* 用于将配置内容添加到Spring的环境中 与@Configuration一起使用
*
* 例如:
* 有个app.properties里有testbean.name=myTestBean
* 使用@Configuration和@PropertySource将app.properties提供给Environment
*
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/myco/app.properties")
* public class AppConfig {
*
* @Autowired
* Environment env;
*
* @Bean
* public TestBean testBean() {
* TestBean testBean = new TestBean();
* testBean.setName(env.getProperty("testbean.name"));
* return testBean;
* }
* }
*
* 解析${...}和@Value注释中的占位符
* 为了使用PropertySource中的属性解析定义中的${...}占位符或@Value注释,
* 必须确保在ApplicationContext使用的BeanFactory中注册了适当的嵌入值解析器,
* 可以通过静态@Bean方法显式注册PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer来实现,
* 但是请注意,通常仅当您需要自定义配置(例如占位符语法等)时才需要通过静态
*
* 例如:
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/${my.placeholder:default/path}/app.properties")
* public class AppConfig {
* @Autowired
* Environment env;
*
* @Bean
* public TestBean testBean() {
* TestBean testBean = new TestBean();
* testBean.setName(env.getProperty("testbean.name"));
* return testBean;
* }
* }
*
* 如果给定的属性键存在于多个 .properties文件中,
* 则处理的最后一个 @PropertySource 注释并覆盖
*
* 例如:
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/myco/a.properties")
* public class ConfigA { }
*
* @Configuration
* @PropertySource("classpath:/com/myco/b.properties")
* public class ConfigB { }
*
* 覆盖顺序取决于这些类在应用程序上下文中注册的顺序。
* AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
* ctx.register(ConfigA.class);
* ctx.register(ConfigB.class);
* ctx.refresh();
*
* 在上面的场景中,b.properties 中的属性将覆盖 a.properties 中存在的任何重复项
* 因为 ConfigB 是最后注册的。
*
* 在某些情况下,在使用@PropertySource注释时严格控制属性源排序可能是不可能或不切实际的
* 例如,如果上面的 @Configuration 类是通过组件扫描注册的,则很难预测其顺序
* 在这种情况下-如果覆盖很重要建议ConfigurableEnvironment和MutablePropertySources
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(PropertySources.class)
public @interface PropertySource {
/**
* 指明此属性源的名称
* 如果省略,factory()将根据底层资源生成一个名称
* (就org.springframework.core.io.support.DefaultPropertySourceFactory而言;
* 通过org.springframework.core.io.support.ResourcePropertySource无参构造函数)
*/
String name() default "";
/**
* 指示要加载的属性文件的资源位置。
* 支持 properties 和 xml 文件格式 — 例如,“classpath:/com/myco/app.properties”或“file:/path/to/file.xml”
* 不允许使用资源位置通配符(例如 **/*.properties)
* 每个位置必须精确评估为一个 .properties 资源
* ${...} 占位符将针对已在环境中注册的任何/所有属性源进行解析
*/
String[] value();
/**
* 是否忽略未找到的property资源
* 默认为false
* /
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound() default false;
/**
* 给定资源的特定字符编码,例如 "UTF-8"。
* properties文件的编码默认是ios8859-1
*/
String encoding() default "";
/**
* 指定自定义的PropertySourceFactory
* 如果想要指定yml等其他格式的文件需要自定义实现
*/
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factory() default PropertySourceFactory.class;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
# 三:自定义PropertySourceFactory
下面例子采用的都是 yml 格式,所以需要自定义 PropertySourceFactory 用来解析 yml
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.YamlPropertiesFactoryBean;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertiesPropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.DefaultPropertySourceFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.EncodedResource;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
public class YmlConfigFactory extends DefaultPropertySourceFactory {
@Override
public PropertySource<?> createPropertySource(String name, EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
String sourceName = name != null ? name : resource.getResource().getFilename();
if (!resource.getResource().exists()) {
return new PropertiesPropertySource(sourceName, new Properties());
} else if (sourceName.endsWith(".yml") || sourceName.endsWith(".yaml")) {
Properties propertiesFromYaml = loadYml(resource);
return new PropertiesPropertySource(sourceName, propertiesFromYaml);
} else {
return super.createPropertySource(name, resource);
}
}
private Properties loadYml(EncodedResource resource) throws IOException {
YamlPropertiesFactoryBean factory = new YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
factory.setResources(resource.getResource());
factory.afterPropertiesSet();
return factory.getObject();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
# 四:@Value
三种用法:
- 直接赋值:@Value("ccj")
- 读取配置文件:@Value("${demo1.name}")
- 指定默认值:@Value("${demo1.name:ccj}") 表示如果没有demo1.name的配置,则赋值为ccj
- SPEL表达式:@Value("#{'${demo1.name}'?.toUpperCase()}") 表示将从配置文件读取的值转为大写,?可以不填,表示如果没有demo1.name的配置,则忽略
application.yml
## demo1
demo1:
name: ccj
address: guangzhou
like: comic,coding,movie
2
3
4
5
TestController.java
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Arrays;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Value("${demo1.name}")
private String demo1Name;
@Value("${demo1.address}")
private String demo1Address;
@Value("#{'${demo1.like}'.split(',')}")
private String demo1Like1;
@Value("${demo1.like}")
private String[] demo1Like2;
@GetMapping("/demo1")
public String demo1() {
return String.format("name:%s<br/>address:%s<br/>like1:%s<br/>like2:%s", demo1Name, demo1Address, demo1Like1, Arrays.toString(demo1Like2));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
运行结果:

不支持复杂类型,例如 List、Map
# 五:Environment
application.yml
## demo2
demo2:
name: qform
address: huizhou
like: eating,running
2
3
4
5
TestController.java
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
Environment environment;
@GetMapping("/demo2")
public String demo2() {
String name = environment.getProperty("demo2.name");
String address = environment.getProperty("demo2.address");
List like = environment.getProperty("demo2.like", List.class);
return String.format("name:%s<br/>address:%s<br/>like:%s", name, address, like);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
运行结果:

不支持复杂类型,例如 Map
# 六:@ConfigurationProperties
类的字段必须有public setter方法
根据 Spring Boot 宽松的绑定规则,类的属性名称必须与外部属性的名称匹配
demo3.yml
## demo3
demo3:
name: ccj
address: jieyang
like:
- comic
- eating
- coding
- movie
- 佛系
map1: { key1: v1, key2: v2 }
map2:
key3: v3
key4: v4
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
Demo3.java
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.util.List;
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = {"classpath:demo3.yml"}, encoding = "UTF-8", factory = YmlConfigFactory.class)
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "demo3")
public class Demo3 {
private String name;
private String address;
private List<String> like;
private Map<String, String> map1;
private Map<String, String> map2;
// Getter 和 Setter忽略
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
TestController.java
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
Demo3 demo3;
@GetMapping("/demo3")
public String demo3() {
return String.format("name:%s<br/>address:%s<br/>like:%s<br/>map1:%s<br/>map2:%s", demo3.getName(), demo3.getAddress(), demo3.getLike(), demo3.getMap1(), demo3.getMap2());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
运行结果:
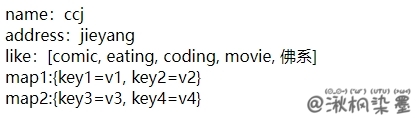
# 七:PropertiesLoaderUtils
demo4.properties
## demo4
demo4.name: demo4Name
demo4.address: demo4Address
2
3
TestController.java
@RestController
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("/demo4")
public String demo4() throws IOException {
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties("demo4.properties");
return String.format("name:%s<br/>address:%s", properties.getProperty("demo4.name"), properties.getProperty("demo4.address"));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
运行结果:

如果Map类型的key包含非字母数字和-的字符,需要用单/双引号括起来
# 八:Configuration Processor
在使用 @ConfigurationProperties 时,idea一般会提示如下警告
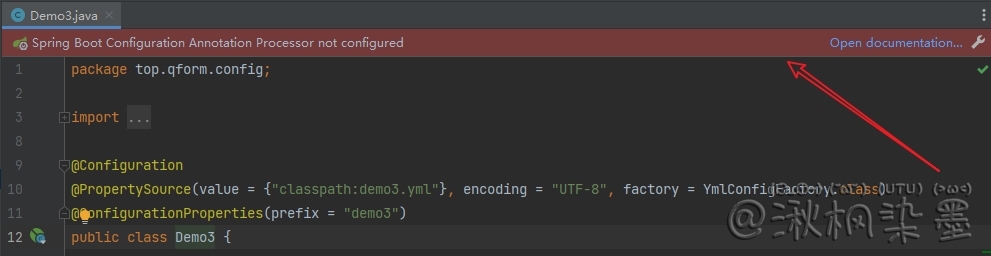
原因:SpringBoot1.5 以上版本 @ConfigurationProperties 取消 location 注解
解决方案:使用 spring-boot-configuration-processor 在编译时自动产生 @ConfigurationProperties 标记的类的Metadata,用于提供给IDE在自动提示。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
重新 build 项目之后,configuration processor 会创建一个 JSON 文件:
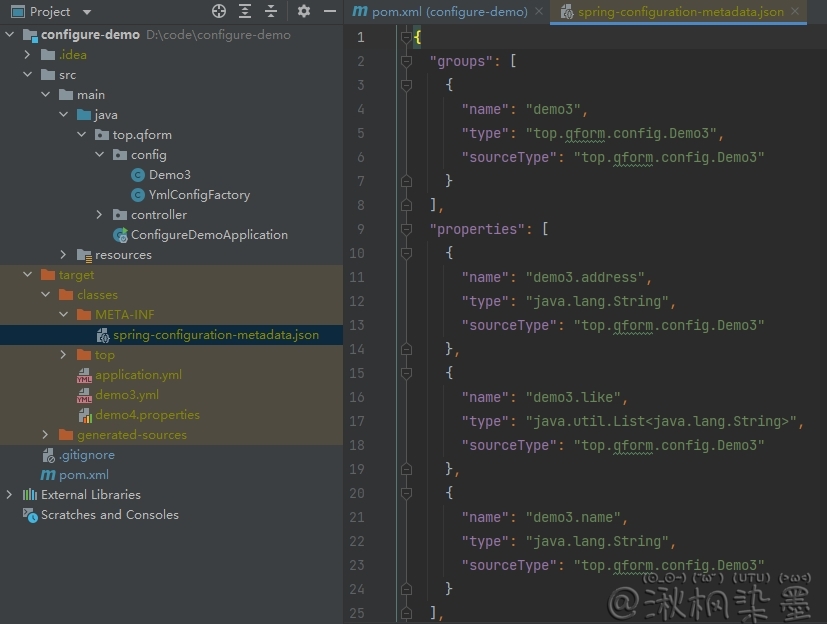
由于 spring-boot-configuration-processor 程序执行时用不到,所以从 spring-boot-maven-plugin 中排除,这样构建时才不会被打包。
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 九:拓展
# 9.1 @DurationUnit
从配置参数中解析 durations(持续时间),既可以配置毫秒数数值,也可配置带有单位的文本。
常用单位如下:
nsfor nanoseconds (纳秒)usfor microseconds (微秒)msfor milliseconds (毫秒)sfor seconds (秒)mfor minutes (分)hfor hours (时)dfor days (天)
# 9.2 @DataSize
与 Duration 的用法一样,默认单位是 byte (字节),可以通过 @DataSizeUnit 单位指定。
Bfor bytesKBfor kilobytesMBfor megabytesGBfor gigabytesTBfor terabytes
# 9.3 示例
demo5.yml
## demo5
demo5:
duration1: 2s
duration2: 5
dataSize1: 2MB
dataSize2: 5
2
3
4
5
6
TestController.java
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
Demo5 demo5;
@GetMapping("/demo5")
public String demo5() {
return String.format("duration1:%s<br/>duration2:%s<br/>dataSize1:%s<br/>dataSize2:%s", demo5.getDuration1(), demo5.getDuration2(), demo5.getDataSize1(), demo5.getDataSize2());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
运行结果:
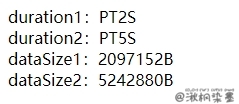
# 9.4 @DeprecatedConfigurationProperty
标记某个属性为 deprecated
可以通过添加 @DeprecatedConfigurationProperty 注解到字段的 getter 方法上,来标示该字段为 deprecated,重新 build 项目,看看 JSON 文件发生了什么?
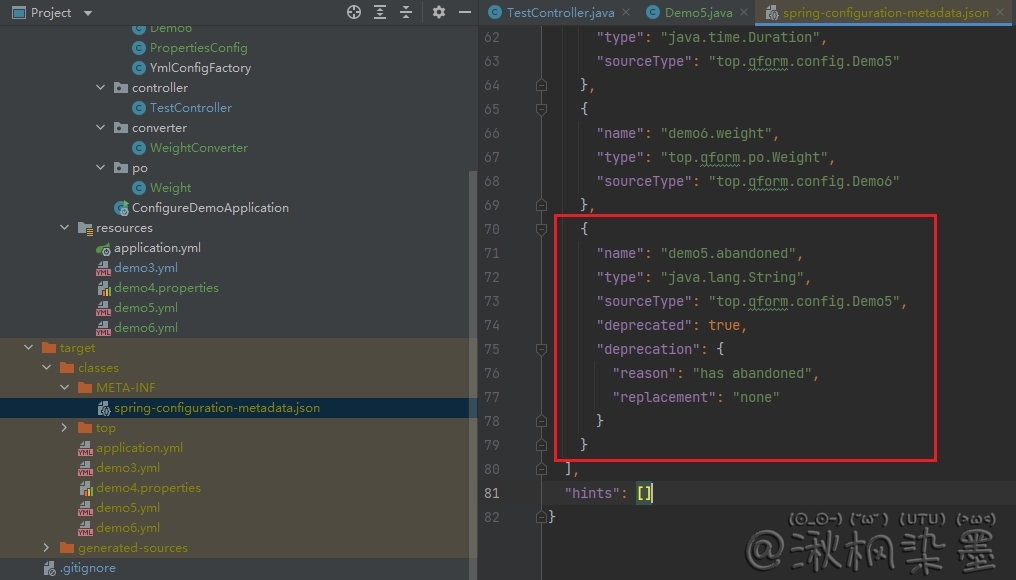
# 十:自定义
解析配置参数到自定义的对象类型上
例如:新增一个 Weight 类来设置最大包裹重量
Weight.java
public class Weight {
private String value;
public Weight(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Weight{" +
"value='" + value + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
WeightConverter.java(转换器)
public class WeightConverter implements Converter<String, Weight> {
@Override
public Weight convert(String s) {
return new Weight("Max:" + s);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
PropertiesConfig.java(注入到Spring上下文)
@Configuration
public class PropertiesConfig {
@Bean
@ConfigurationPropertiesBinding
public WeightConverter getWeightConverter() {
return new WeightConverter();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
TestController.java
@RestController
public class TestController {
@Autowired
Demo6 demo6;
@GetMapping("/demo6")
public String demo6() {
return String.format("weight:%s", demo6.getWeight());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
运行结果:
# 十一:总结:
- properties文件默认使用的是iso8859-1,并且不可修改
- yml文件的加载顺序高于properties,但是读取配置信息的时候会读取后加载的
- @PropertySource注解默认只会加载properties文件
- @PropertySource注解可以与任何一种方式联合使用
- 简单值推荐使用@Value,复杂对象推荐使用@ConfigurationProperties
- 示例代码:configure-demo (opens new window)
