摘要
JDK:1.8.0_202
Spring Version:5.2.11.RELEASE
# 一:前言
下面介绍 SpringBoot 项目在启动时预加载资源的多种方式
# 二:Java
# 2.1 static 代码块
static静态代码块,在类加载的时候即自动执行。
# 2.2 构造方法
在对象初始化时执行。执行顺序在static静态代码块之后。
# 三:Spring
# 3.1 @PostConstruct
@PostConstruct 注解使用在方法上,这个方法在对象依赖注入初始化之后执行。
顺序为:constructer > @Autowired > @PostConstruct
特点:
- 一个类只能有一个非静态方法使用此注解
- 被注解的方法不得有任何参数
- 被注解的方法返回值必须为void
- 被注解的方法不得抛出已检查异常
- 此方法只能被执行一次
PostConstructTest:
@Component
public class PostConstructTest {
static {
System.out.println("static");
}
public PostConstructTest() {
System.out.println("constructer");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PostConstruct");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
# 3.2 CommandLineRunner
SpringBoot提供了两个接口来实现Spring容器启动完成后执行的功能,两个接口分别为CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner。
其实质为容器启动后回调,类似于开机自启动
这两个接口需要实现一个run方法,将代码在run中实现即可。这两个接口功能基本一致,其区别在于run方法的入参。ApplicationRunner的run方法入参为ApplicationArguments,为CommandLineRunner的run方法入参为String数组。
Order注解:
当有多个类实现了 CommandLineRunner 和 ApplicationRunner 接口时,可以通过在类上添加 @Order 注解来设定运行顺序。且value值越小则优先级越高。
CommandLineRunner 接口源码:
package org.springframework.boot;
/**
* 当 bean 包含在 SpringApplication 中时,该接口用于指示 bean 应该运行。
* 在同一个应用程序上下文中可以定义多个 CommandLineRunner bean,
* 并且可以使用 Ordered 接口或 @Order 注释进行排序。
* 如果需要访问 ApplicationArguments 而不是原始字符串数组,请考虑使用 ApplicationRunner。
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
/**
* 用于运行 bean 的回调。
* @param args 传入main方法的参数
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
测试类:(CommandLineRunnerTest.java)
@Component
@Order(2)
public class CommandLineRunnerTest implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
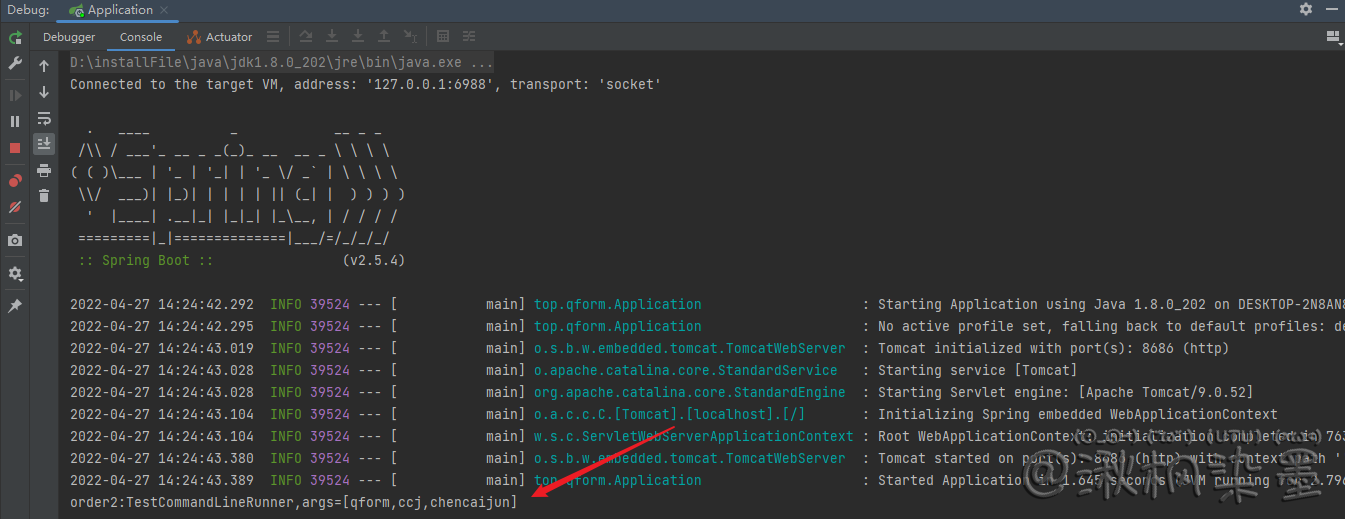
System.out.println("order2:TestCommandLineRunner,args=" + Arrays.toString(args));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
配置参数后启动:

运行结果:
# 3.3 ApplicationRunner
ApplicationRunner 接口源码:
package org.springframework.boot;
/**
* 与 CommandLineRunner 一样
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationRunner {
/**
* 与 CommandLineRunner 一样
*/
void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
ApplicationArguments 接口源码:
/**
* 提供对用于运行SpringApplication的参数的访问
*/
public interface ApplicationArguments {
/**
* 返回传递给应用程序的未经处理的原始参数
*/
String[] getSourceArgs();
/**
* 返回所有选项参数的名称
* 例如,如果参数是 "--foo=bar --debug" 返回值为 ["foo", "debug"]
* @return 选项名称或空集
*/
Set<String> getOptionNames();
/**
* 返回参数解析的选项参数集是否包含具有给定名称的选项
*
* @param name 要检查的名称
* @return 如果参数包含给定名称的选项,则为 true
*/
boolean containsOption(String name);
/**
* 返回与具有给定名称的参数选项关联的值的集合
*
* 如果选项存在并且没有参数(例如:"--foo"),则返回一个空集合([])
* 如果该选项存在并且只有一个值(例如:"--foo=bar”),则返回一个包含一个元素的集合(["bar"])
* 如果该选项存在并且具有多个值(例如"--foo=bar --foo=baz"),则返回一个包含每个值的元素的集合(["bar","baz"])
* 如果该选项不存在,则返回 null
*
* @param name 选项的名称
* @return 给定名称的选项值列表
*/
List<String> getOptionValues(String name);
/**
* 返回已解析的非选项参数的集合。
* @return 非选项参数或空列表
*/
List<String> getNonOptionArgs();
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
测试类:(ApplicationRunnerTest.java)
@Component
@Order(1)
public class ApplicationRunnerTest implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) throws Exception {
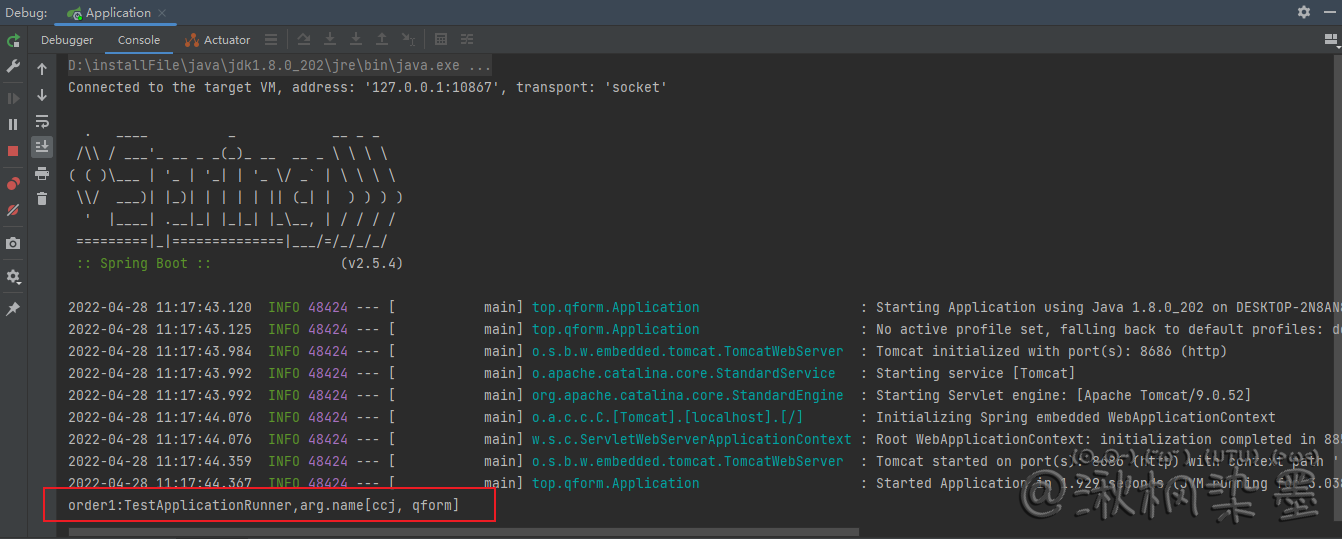
System.out.println("order1:TestApplicationRunner,arg.name" + applicationArguments.getOptionValues("name"));
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
配置参数后启动:

运行结果:
# 3.3 InitializingBean
InitializingBean接口为bean提供了初始化方法的方式,它只包括afterPropertiesSet方法,凡是继承该接口的类,在初始化bean的时候会执行该方法。
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
/**
* 由 BeanFactory 设置所有属性后需要对做出反应的 bean 实现的接口
* 例如:执行自定义初始化,或仅检查是否已设置所有必需属性
* 实现 InitializingBean 的另一种方法是指定自定义 init 方法,例如在 XML bean 定义中
*/
public interface InitializingBean {
/**
* 在设置所有 bean 属性并满足 BeanFactoryAware、ApplicationContextAware 等后由包含 BeanFactory 调用
* 此方法允许 bean 实例在设置所有 bean 属性后执行其整体配置和最终初始化的验证
* @throws Exception 在配置错误的情况下(例如未能设置基本属性)或由于任何其他原因初始化失败
*/
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
测试类:(InitializingBeanTest.java)
@Component
public class InitializingBeanTest implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
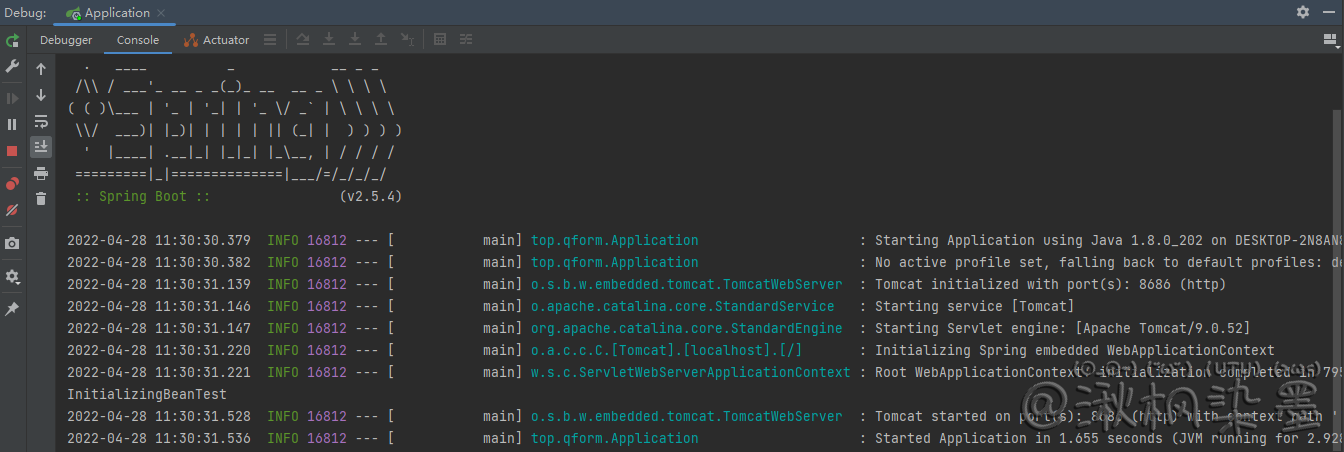
System.out.println("InitializingBeanTest");
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
运行结果:
# 四:测试
将上面所有测试类,放在同一项目中运行
运行结果:

其中 static 代码,constructer,@PostConstruct, InitializingBean 是在启动过程中执行代码
ApplicationRunner 与 CommandLineRunner 是在启动后运行的功能
# 五:小结
Spring应用启动过程中,肯定是要自动扫描有@Component注解的类,加载类并初始化对象进行自动注入。加载类时首先要执行static静态代码块中的代码,之后再初始化对象时会执行构造方法。
在对象注入完成后,调用带有@PostConstruct注解的方法。当容器启动成功后,再根据**@Order**注解的顺序调用CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner接口类中的run方法。
因此,加载顺序为static>constructer>@PostConstruct>CommandLineRunner和ApplicationRunner.
